For their first Slow Art Day the IAACC Pablo Serrano in Zaragoza, Spain, highlighted four works by female photographers from the Museum’s archive:
- Grete Stern, Sueño 39, 1949.
- Cristina Martín Lara, “Si yo supiera a qué se debe…/ Wenn ich nur wüsste woran das liegt…(1) II”, 2004.
- Mapi Rivera, “Estelación crepuscular”, 2004.
- Liang Yuanwei, “S/T, Series: ‘Don’t forget to say you love me’, 2005.
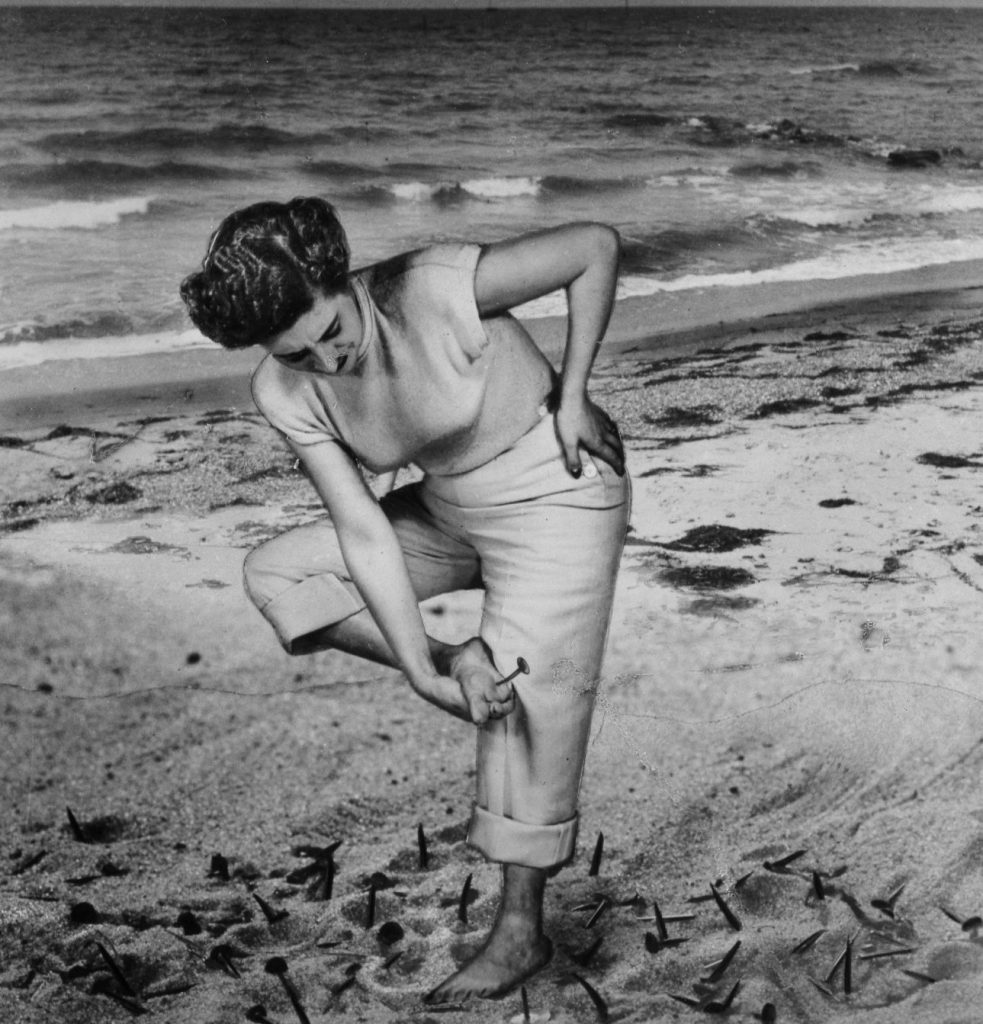
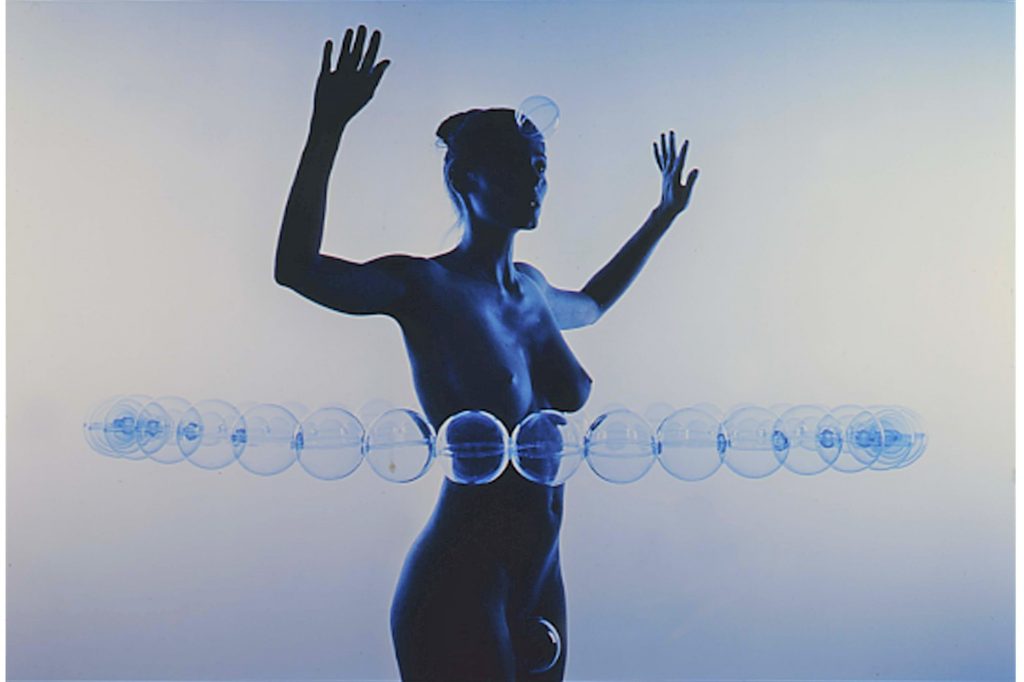




The photos were part of the virtual project “Visiones transversales en torno a Circa XX. A través de mi cuerpo / A través de tu cuerpo” (“Transversal visions circa XX. Through my body / Through your body”) which explores women, their physical bodies, as well as their social and artistic agency.
For example, Stern’s “Sueño 39” denounces obstacles women faced in 1940s Argentina. Yuanwei’s self-portrait series “Don’t forget to say you love me” is a parody of erotic photographs of women which comments on the male gaze and the objectification of women.
On April 4th, 2020, the photos were shared on social media, accompanied by prompts and brief descriptions. Viewers were encouraged to look slowly at each photograph and then to share their reflections online. The Museum also produced a short video of the four works, which can be viewed below.
The photos were liked many times on social media and some participants, and even some artists, posted inspiring reflections. One of the photographers, Cristina Martín Lara, commented on Facebook:
What a joy to be part of this Slow Art Day initiative to show everyone the Cirka XX Collection in our confinement. Thank you for making it possible! (Translated from Spanish)
Cristina Martín Lara
Several participants also posted reflections in connection with individual photographs. For example:
Even in the most idyllic context we can find something that makes us stop suddenly, causing us pain that only time, and not the context, can mitigate. (Translated from Spanish)
Participant response to Grete Stern’s “Sueño 39”, Instagram.
At Slow Art Day HQ we are inspired by the depth of symbolism in these photographs. The works in the Cirka XX project are exciting to consider one-by-one and even more powerful when viewed in relation to each other. We recommend that all Slow Art Day readers look at the photos posted above as well as the video.
We want to also thank María Luisa Grau Tello, curator at IAACC Pablo Serrano, as well as Julio Ramón Sanz, Eva María Alquézar, Alba Rodrigo Urmente, Gloria Sánchez Martín, Silvia Abad Villarroya and Alfredo Blanco Morte for hosting the Museum’s innagural Slow Art Day event.
We look forward to what the IAACC comes up with for Slow Art Day in 2021!
– Johanna and Ashley